08.大模型Function Call的应用
OpenAI于2023年6月推出的FunctionCall功能使GPT-4/3.5-turbo能通过JSON对象调用外部函数,解决了大模型的信息实时性、数据局限性和功能扩展性问题。文章详细介绍了FunctionCall的工作原理,通过查询天气、航班信息和SQL数据库三个实践案例,展示了如何定义函数、描述参数并实现交互。案例代码包括函数调用流程、参数传递及结果处理,证明FunctionCall能有效
1 什么是Function Call
2023年6月13日 OpenAI 公布了 Function Call(函数调用) 功能,Function Call 允许开发者向 GPT-4 和 GPT-3.5-turbo 模型描述函数,模型会智能地选择输出一个包含调用这些函数参数的JSON对象。这是一种更可靠地将 GPT 的功能与外部工具和 API 相连接的新方法。
GPT4 及 GPT-3.5-turbo 模型之所以能够使用函数 Function Call 功能,是因为这些模型经过训练,不仅可以检测到何时需要调用函数(根据用户的输入),并且又可以回复符合函数参数的 JSON对象,而不是直接返回常规的文本,简而言之:函数调用使开发者能够更可靠地从模型中获得结构化数据。
那么 Function Call 可以解决大模型什么问题:
- 信息实时性:大模型训练时使用的数据集往往有时间限制,无法包含最新的信息,如最新的新闻、实时股价等。通过Function Call,模型可以实时获取最新数据,提供更加时效的服务。
- 数据局限性:模型的训练数据量庞大但有限,无法覆盖所有可能的查询,如医学、法律等领域的专业咨询。Function Call允许模型调用外部数据库或API,获取特定领域的详细信息。
- 功能扩展性:大模型虽然功能强大,但不可能内置所有可能需要的功能。通过Function Call,可以轻松扩展模型能力,如调用外部工具进行复杂计算、数据分析等。
总的来说,Function Call功能的出现,极大地提升了大型语言模型的实用性和灵活性,使其能够更好地服务于用户的各种需求。
2 Function Call 工作原理
接下来,我们通过举例分别对比有无Function Call功能时GPT模型工作流程的差异:
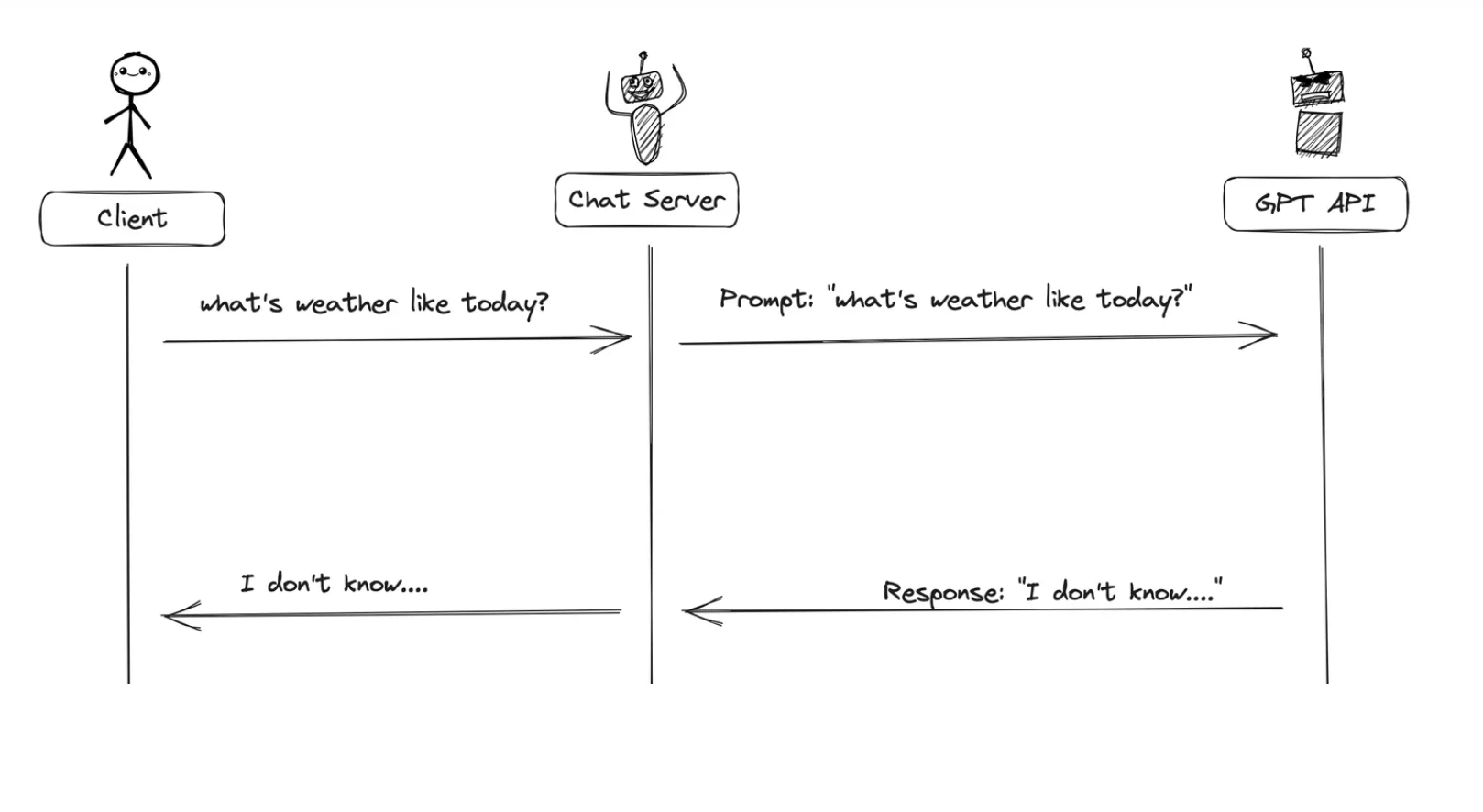
当没有函数调用(funciton-call)时候,我们调用GPT构建AI应用的模式非常简单。
-
主要步骤:
-
用户(client)发请求给我们的服务(chat server)
- 我们的服务(chat server)给GPT提示词
- 重复执行
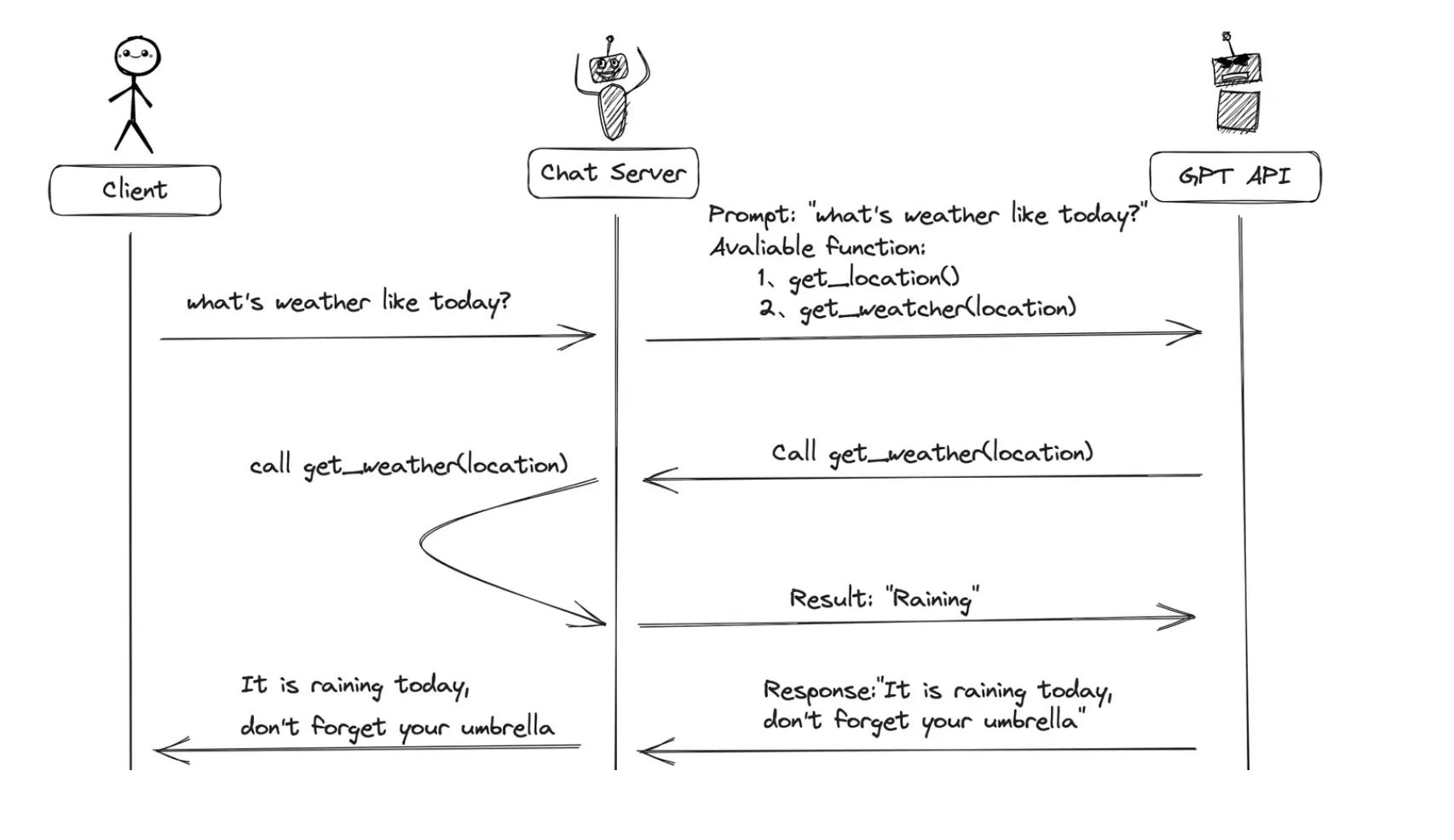
当有函数调用(funciton-call)时候,我们调用GPT构建AI应用的模式比之前要复杂一些。
-
主要步骤:
-
用户(client)发请求提示词以及可以调用的函数给我们的服务(chat server)
- GPT模型根据用户的提示词,判断是用普通文本还是函数调用的格式响应我们的服务(chat server)
- 如果是函数调用格式,那么Chat Server就会执行这个函数,并且将结果返回给GPT
- 然后模型使用提供的数据,用连贯的文本响应。返回
3 Function Call 实践应用
假设我们要创建一个具备查询实时天气的聊天机器人。
3.1 定义外部函数
- 查询某地的天气函数:get_current_weather(location: str)
import json
import requests
# 城市名称对应的编码
data = [
{
"city_name": "北京",
"city_code": "101010100"
},
{
"city_name": "昌平",
"city_code": "101010700"
},
{
"city_name": "广州",
"city_code": "101280101"
}
]
def get_current_weather(location):
"""得到给定地址的当前天气信息"""
# 根据location 匹配city_name, 如果找到,则返回对应的city_code,如果没找到city_code为空字符串
city_code = ""
for loc in data:
if location == loc["city_name"]:
city_code = loc["city_code"]
# 没有匹配到,直接返回
if city_code == "":
return json.dumps({"location": location, "code": 0, "result": {}}, ensure_ascii=False)
# 否则获取天气信息
weather_url = "http://t.weather.itboy.net/api/weather/city/" + city_code
response = requests.get(weather_url)
result1 = json.loads(response.text)
forecast = result1["data"]["forecast"][0]
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"high_temperature": forecast["high"],
"low_temperature": forecast["low"],
"week": forecast["week"],
"type": forecast["type"],
}
return json.dumps({
"location": location,
"code": 1,
"result": weather_info}, ensure_ascii=False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(get_current_weather("广州"))
3.2 描述函数功能
- 为了向模型描述外部函数库,需要向 tools 字段传入可以调用的函数列表。参数如下表:
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 是否必填 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | 是 | 设置为function |
| function | Object | 是 | |
| name | String | 是 | 函数名称 |
| description | String | 是 | 用于描述函数功能,模型会根据这段描述决定函数调用方式。 |
| parameters | Object | 是 | parameters字段需要传入一个Json Schema对象,以准确地定义函数所接受的参数。若调用函数时不需要传入参数,省略该参数即可。 |
| required | 否 | 指定哪些属性在数据中必须被包含。 |
样例:
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市或区,例如北京、海淀",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
}
]
3.3 模型应用Function Call
3.3.1创建 client
- 这里默认使用ZhipuAI,第一次注册免费赠送100万token,没有 key 可以自己去 智谱开发平台注册一下。
3.3.2 模型应用(第一次)
- 第一次模型得到回复时符合函数参数的 JSON对象
- 比如:我们想查询"今天北京的天气如何?"。我们向模型提供这个信息:
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv(".env")
client = OpenAI(api_key=os.environ.get("ZHIPUAI_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/")
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个天气播报小助手,你需要根据用户提供的地址来回答当地的天气情况,如果用户提供的问题具有不确定性,不要自己编造内容,提示用户明确输入"})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "今天北京的天气如何?"})
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市或区,例如北京、海淀",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
}
]
def chat_completion_request(messages, tools, tool_choice):
"""
Send a ChatCompletion request to the OpenAI API
"""
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="GLM-4-Flash-250414",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice=tool_choice,
)
chat_completion = chat_completion_request(messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto")
# 模型返回结果:
print(chat_completion.choices[0].message)
"""
ChatCompletionMessage(content='{"index":0,"finish_reason":"tool_calls","delta":{"role":"assistant","content":null,"reasoning_content":null,"audio":null,"tool_calls":[{"id":"call_20250729104924da7593846f6544d3_0","index":0,"type":"function","function":{"name":"get_current_weather","arguments":"{\\"location\\": \\"北京\\"}","outputs":null},"code_interpreter":null,"retrieval":null,"mcp":null,"drawing_tool":null,"web_browser":null,"search_intent":null,"search_result":null}],"tool_call_id":null,"attachments":null,"metadata":null}}', refusal=None, role='assistant', annotations=None, audio=None, function_call=None, tool_calls=[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_-8481825350119211342', function=Function(arguments='{"location": "北京"}', name='get_current_weather'), type='function', index=0)])
"""
关于 tool_choice 如果不写,则默认情况下模型将决定何时适合使用其中一个函数。
如果要控制模型如何选择函数调用,需要设置 tool_choice 参数。参数默认值为auto,此时模型根据上下文信息自行选择是否返回函数调用。
若将其设置为 {"name": "your_function_name"} 时,可以强制 API 返回特定函数的调用。
还可以通过将 tool_choice 参数设置为 "none" 来强制 API 不返回任何函数的调用。
- 可以看到此时**模型成功触发对 get_current_weather 函数的应用** 参数为location=北京"。
3.3.3 定义处理 Function call 的函数
- 本质 Function call,就是通过大模型选择函数以及获取函数的参数。然后进行函数的运行
def parse_response(response):
response_message = response.choices[0].message
# 检测是否需要调用函数
if response_message.tool_calls:
# 调用函数
available_functions = {
"get_current_weather": get_current_weather,
} # only one function test in this example, but you can have multiple
function_name = response_message.tool_calls[0].function.name
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(response_message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments)
function_response = fuction_to_call(
location=function_args.get("location"),
)
return function_response
上述parse_response函数得到真实函数运行的结果
{"location": "北京", "code": 1, "result": {"location": "北京", "high_temperature": "高温 34℃", "low_temperature": "低温 24℃", "week": "星期二", "type": "中雨"}}
3.3.4 模型应用(第二次)
- 基于上下文以及函数返回的结果,重新作为prompt输入模型,得到最终的结果
# extend conversation with assistant's reply
assistant_message = chat_completion.choices[0].message
print(f'assistant_message-->{assistant_message}')
# extend conversation with assistant's reply
messages.append(assistant_message.model_dump())
function_name = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.name
print(f'function_name--》{function_name}')
function_id = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].id
print(f'function_id--》{function_id}')
function_response = parse_response(response)
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": function_id,
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
) # extend conversation with function response
last_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto"
)
print(f'last_response--》{last_response.choices[0].message}')
3.4 Function Call应用完整代码
- 该 Function Call 应用目的:创建一个具备查询实时天气的聊天机器人。
- 完整代码包含两个部分:一个main.py、tools.py。另外还包含一个cityCode的json文件,该文件的目的是实现城市名称到城市编码的映射,因为天气接口API是只能基于编码的结果进行查询。
tools.py脚本内容为:
import json
import requests
# 城市名称对应的编码
data = [
{
"city_name": "北京",
"city_code": "101010100"
},
{
"city_name": "昌平",
"city_code": "101010700"
},
{
"city_name": "广州",
"city_code": "101280101"
}
]
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市或区,例如北京、海淀",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
}
]
def get_current_weather(location):
"""得到给定地址的当前天气信息"""
# 根据location 匹配city_name, 如果找到,则返回对应的city_code,如果没找到city_code为空字符串
city_code = ""
for loc in data:
if location == loc["city_name"]:
city_code = loc["city_code"]
# 没有匹配到,直接返回
if city_code == "":
return json.dumps({"location": location, "code": 0, "result": {}}, ensure_ascii=False)
# 否则获取天气信息
weather_url = "http://t.weather.itboy.net/api/weather/city/" + city_code
response = requests.get(weather_url)
result1 = json.loads(response.text)
forecast = result1["data"]["forecast"][0]
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"high_temperature": forecast["high"],
"low_temperature": forecast["low"],
"week": forecast["week"],
"type": forecast["type"],
}
return json.dumps({
"location": location,
"code": 1,
"result": weather_info}, ensure_ascii=False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(get_current_weather("北京"))
main.py 的内容为:
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from tools import get_current_weather, tools
import json
load_dotenv(".env")
client = OpenAI(api_key=os.environ.get("ZHIPUAI_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/")
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个天气播报小助手,你需要根据用户提供的地址来回答当地的天气情况,如果用户提供的问题具有不确定性,不要自己编造内容,提示用户明确输入"})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "今天北京的天气如何?"})
def chat_completion_request(messages, tools, tool_choice):
"""
Send a ChatCompletion request to the OpenAI API
"""
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="GLM-4-Flash-250414",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice=tool_choice,
)
def parse_response(response):
response_message = response.choices[0].message
# 检测是否需要调用函数
if response_message.tool_calls:
# 调用函数
available_functions = {
"get_current_weather": get_current_weather,
} # only one function test in this example, but you can have multiple
function_name = response_message.tool_calls[0].function.name
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(response_message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments)
function_response = fuction_to_call(
location=function_args.get("location"),
)
return function_response
def main():
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个天气播报小助手,你需要根据用户提供的地址来回答当地的天气情况,如果用户提供的问题具有不确定性,不要自己编造内容,提示用户明确输入"})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "今天北京的天气如何"})
print(messages)
response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto"
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
print(f'assistant_message-->{assistant_message}')
# extend conversation with assistant's reply
messages.append(assistant_message.model_dump())
function_name = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.name
print(f'function_name--》{function_name}')
function_id = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].id
print(f'function_id--》{function_id}')
function_response = parse_response(response)
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": function_id,
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
) # extend conversation with function response
last_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto"
)
print(f'last_response--》{last_response.choices[0].message}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
输出结果
last_response--》ChatCompletionMessage(content='今天北京的天气情况如下:中雨,高温 34℃,低温 24℃。这是星期二的天气状况。', refusal=None, role='assistant', annotations=None, audio=None, function_call=None, tool_calls=None)
4 多个Functions的应用实践
- 该 Function Call 应用目的:假设我们要创建一个具备查询航班功能的聊天机器人。
- 完整代码包含三个部分:一个muti_function_zhipu.py、airplane_function_tools.py、muti_utils.py。
- airplane_function_tools.py 定义需要的工具类函数:描述函数功能
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_plane_number",
"description": "根据始发地、目的地和日期,查询对应日期的航班号",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"start": {
"description": "出发地",
"type": "string"
},
"end": {
"description": "目的地",
"type": "string"
},
"date": {
"description": "日期",
"type": "string",
}
},
"required": ["start", "end", "date"]
},
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_ticket_price",
"description": "查询某航班在某日的价格",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"number": {
"description": "航班号",
"type": "string"
},
"date": {
"description": "日期",
"type": "string",
}
},
"required": [ "number", "date"]
},
}
},
]
- muti_utils.py
- 定义两个外部函数供模型选择调用:查询两地之间某日航班号函数:get_flight_number(departure: str, destination: str, date: str);查询某航班某日票价函数:get_ticket_price(flight_number: str, date: str)
- 定义解析Function Call的函数
import json
def get_plane_number(date, start , end):
plane_number = {
"北京": {
"深圳": "126",
"广州": "356",
},
"郑州": {
"北京": "1123",
"天津": "3661",
}
}
return {"date": date, "number": plane_number[start][end]}
def get_ticket_price(date:str , number:str):
print(date)
print(number)
return {"ticket_price": "668"}
def parse_function_call(model_response):
'''
:param model_response: 模型返回的结果
:return: 返回函数的结果
'''
function_result = ''
if model_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
tool_call = model_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
args = tool_call.function.arguments
function_result = {}
if tool_call.function.name == "get_plane_number":
function_result = get_plane_number(**json.loads(args))
if tool_call.function.name == "get_ticket_price":
function_result = get_ticket_price(**json.loads(args))
return function_result
- muti_function_zhipu.py 主逻辑函数
import json
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
from muti_utils import get_plane_number, get_ticket_price, parse_function_call
from airplane_function_tools import tools
import os
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
# 获取环境变量 ZhiPu_API_KEY
zhupu_ak = os.environ['ZHIPUAI_API_KEY']
client = OpenAI(api_key=zhupu_ak, base_url="https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/") # 填写您自己的APIKey
ChatGLM = "GLM-4-Flash-250414"
def chat_completion_request(messages, tools=None, tool_choice=None, model=ChatGLM):
try:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice=tool_choice,
)
return response
except Exception as e:
print("Unable to generate ChatCompletion response")
print(f"Exception: {e}")
return e
def main():
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system",
"content": "现在你是一个航班查询助手,将根据用户问题提供答案,但是不要假设或猜测传入函数的参数值。如果用户的描述不明确,请要求用户提供必要信息 "})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "帮我查询2025年7月30日,郑州到北京的航班的票价, 如果你不知道请调用工具查询"})
# 1.得到第一次回复:调用:get_plane_number函数
first_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto")
assistant_message1 = first_response.choices[0].message
print(f'assistant_message1-->{assistant_message1}')
# 2. 将第一次得到的模型回复结果加入messages
messages.append(first_response.choices[0].message.model_dump())
# 3. 第一次得到函数的结果
first_function = parse_function_call(model_response=first_response)
print(f'first_function--》{first_function}')
tool_call = first_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
# 4. 将函数的结果添加到messages中,继续送入模型问答
messages.append({"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": str(json.dumps(first_function))})
# 5. 第二次调用模型
print(messages)
second_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto")
print(f'second_response--》{second_response.choices[0].message}')
# 6. 将第二次得到函数结果加入信息中
messages.append(second_response.choices[0].message.model_dump())
second_function = parse_function_call(model_response=second_response)
print(f'second_function--》{second_function}')
tool2_call = second_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
# 4. 将函数的结果添加到messages中,继续送入模型问答
messages.append({"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool2_call.id,
"content": str(json.dumps(second_function))})
last_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto")
print(f'last_response--》{last_response.choices[0].message}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
结果输出:
last_response--》ChatCompletionMessage(content='2025年7月30日,从郑州到北京的航班号为1123的票价为668元。', refusal=None, role='assistant', annotations=None, audio=None, function_call=None, tool_calls=None)
5 使用Function Call功能应用Sql查询
- 该 Function Call 应用目的:假设我们要创建一个具备sql语句查询的聊天机器人。
- 完整代码包含三个部分:一个sql_function_tools.py、sql_zhipu.py。
- sql_function_tools.py
- 定义需要的工具类函数:描述函数功能
- 定义表的结构
- 定义表查询的函数
- 定义解析function call函数
import json
import requests
import os
import pymysql
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
# todo: 1.描述数据库表结构(单一个表格)
database_schema_string = """
CREATE TABLE `emp` (
`empno` int DEFAULT NULL, --员工编号, 默认为空
`ename` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, --员工姓名, 默认为空
`job` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,--员工工作, 默认为空
`mgr` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工领导, 默认为空
`hiredate` date DEFAULT NULL,--员工入职日期, 默认为空
`sal` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工的月薪, 默认为空
`comm` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工年终奖, 默认为空
`deptno` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工部分编号, 默认为空
)"""
# todo: 2.描述数据库表结构(多个表格)
database_schema_string1 = """
CREATE TABLE `emp` (
`empno` int DEFAULT NULL, --员工编号, 默认为空
`ename` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, --员工姓名, 默认为空
`job` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,--员工工作, 默认为空
`mgr` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工领导, 默认为空
`hiredate` date DEFAULT NULL,--员工入职日期, 默认为空
`sal` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工的月薪, 默认为空
`comm` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工年终奖, 默认为空
`deptno` int DEFAULT NULL,--员工部分编号, 默认为空
);
CREATE TABLE `DEPT` (
`DEPTNO` int NOT NULL, -- 部门编码, 默认为空
`DNAME` varchar(14) DEFAULT NULL,--部门名称, 默认为空
`LOC` varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL,--地点, 默认为空
PRIMARY KEY (`DEPTNO`)
);
"""
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "ask_database",
"description": "使用此函数回答业务问题,要求输出是一个SQL查询语句",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": f"SQL查询提取信息以回答用户的问题。"
f"SQL应该使用以下数据库模式编写:{database_schema_string1}"
f"查询应该以纯文本返回,而不是JSON。"
f"查询应该只包含MySQL支持的语法。",
}
},
"required": ["query"],
},
}
}
]
# todo:1.连接数据库,进行sql语句的查询
def ask_database(query):
"""连接数据库,进行查询"""
# 1.连接到 MySQL 数据库
print("进入函数内部")
conn = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
port=3306,
user='',
password='密码',
database='数据库名称',
charset='utf8mb4', # 指定游标类,返回结果为字典
)
# 2. 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
print(f'开始测试')
# 3. 执行sql语句测试
# 示例:执行 SQL 查询
# sql = "SELECT * FROM emp"
print(f'query--》{query}')
cursor.execute(query)
# 4. 获取查询结果
result = cursor.fetchall()
# 5.关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 6.关闭连接
conn.close()
return result
# # todo: 2.根据模型回复来确定使用工具函数:
def parse_response(response):
response_message = response.choices[0].message
# 检测是否需要调用函数
if response_message.tool_calls:
# 调用函数
available_functions = {
"ask_database": ask_database
} # only one function test in this example, but you can have multiple
function_name = response_message.tool_calls[0].function.name
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(response_message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments)
function_response = fuction_to_call(
query=function_args.get("query"),
)
return function_response
if __name__ == '__main__':
query = "select count(*) from emp"
a = ask_database(query)
print(a)
- sql_zhipu.py
- 主逻辑函数
from zhipuai import ZhipuAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
from sql_function_tools import *
import os
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
# 获取环境变量 ZhiPu_API_KEY
zhupu_ak = os.environ['zhupu_api']
client = ZhipuAI(api_key=zhupu_ak) # 填写您自己的APIKey
ChatGLM = "glm-4"
def chat_completion_request(messages, tools=None, tool_choice=None, model=ChatGLM):
try:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice=tool_choice,
)
return response
except Exception as e:
print("Unable to generate ChatCompletion response")
print(f"Exception: {e}")
return e
def main():
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "system",
"content": "通过针对业务数据库生成 SQL 查询来回答用户的问题"})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": "查询工资最高的前5员工姓名及相应的工资,及其部门号和部门名称"})
response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto"
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
print(f'assistant_message1-->{assistant_message}')
function_name = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.name
function_id = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].id
function_response = parse_response(response)
print(f'assistant_message.model_dump()-->{assistant_message.model_dump()}')
messages.append(assistant_message.model_dump()) # extend conversation with assistant's reply
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": function_id,
"name": function_name,
"content": str(function_response),
}
) # extend conversation with function response
print(f'messages-->{messages}')
last_response = chat_completion_request(
messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto"
)
print(f'last_response--》{last_response}')
print(f'last_response--》{last_response.choices[0].message}')
print(f"{last_response.choices[0].message.content}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
输出结果为:
工资最高的前5员工信息如下:
1. 员工姓名:David Anderson,工资:14955,部门号:9,部门名称:SUPPORT
2. 员工姓名:Ian Jones,工资:14949,部门号:6,部门名称:MARKETING
3. 员工姓名:Eva Brown,工资:14915,部门号:10,部门名称:ADMIN
4. 员工姓名:Charlie Anderson,工资:14912,部门号:2,部门名称:ACCOUNTING
5. 员工姓名:Eva Jones,工资:14912,部门号:1,部门名称:SALES
6 小节总结
本章节介绍了大模型 Function call 功能的基本概念和使用方法,包括定义外部函数、描述函数功能、代码编写等。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)